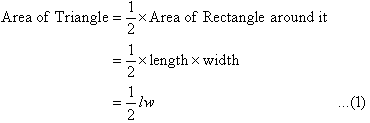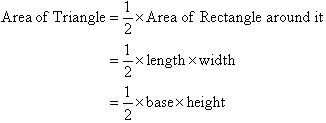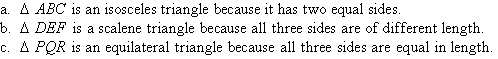Tuesday, July 26, 2011
ENGINEERING DRAWING ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
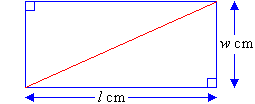
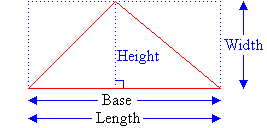
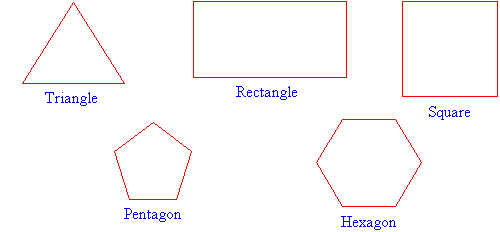
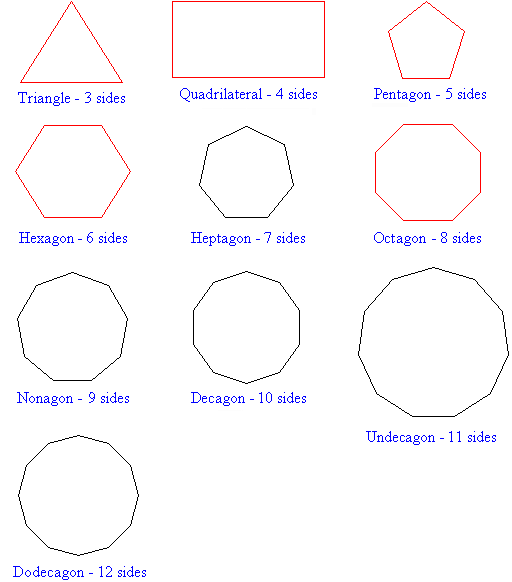
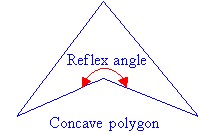
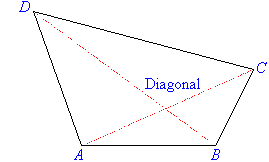
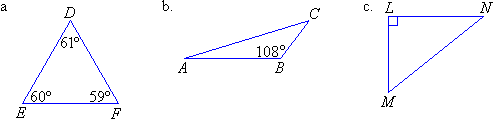
Polygons
ENGINEERING DRAWING ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
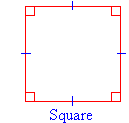
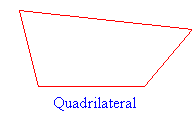
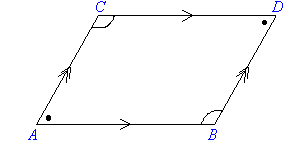
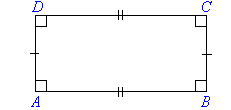
Quadrilaterals
ENGINEERING DRAWING ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
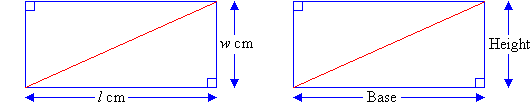
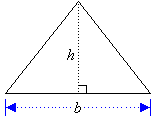
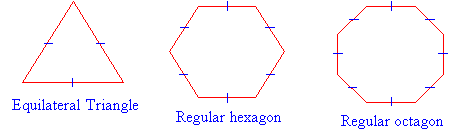
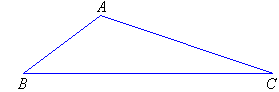
Triangles
Wednesday, July 20, 2011
CIVIL ENGINEERING MCQs
1. A mixture of cement, gravel, coarse sand and water is called
(a) mortar
(b) concrete
(c) slurry
(d) hardner
Ans. (b)
2. RCC is
(a) the concrete having an iron framework inside it as a support
(b) the crushed cement in which more gravel is added
(c) prepared by adding calcium chloride to the limestone and calcium silicate
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a)
3. The process of making soap by the hydrolysis of fats and oils with alkalis is called
(a) hydrolysis
(b) saponification
(c) esterification
(d) none of the above
Ans. (b)
4. The soap can be hardened by
(a) adding sodium carbonate or sodium silicate during its manufacture
(b) adding sodium chloride
(c) adding potassium hydroxide
(d) adding animal fat and coconut oil
Ans. (a)
5. Endoscope is made up of
(a) glass wool
(b) optical fibres
(c) optical glass
(d) lead crystal glass
Ans. (b)
6. The plastics which soften upon being heated but regains all its original properties on
cooling are known as
(a) thermoplastics
(b) thermosetting plastics
(c) thermoelastic
(d) cellulose
Ans. (a)
7. Which of the following is not a thermoplastic polymer?
(a) Nylon
(b) PVC
(c) Polythene
(d) Bakelite
Ans. (d)
8. Match the following:
I II
(A) Heat resistant 1. Used as insulating
Glass material in oven
(B) Glass wool 2. Useful as sun shield
(C) Laminated glass 3. Borosilicate glass
(D) Photochromatic 4, Used in bullet proof
glass screens
A B C D
(a) 2 4 1 3
(b) 3 1 4 3
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 3 2 1 4
Ans. (c)
9. Limestone on heating gives
(a) washing soda
(b) plaster of Paris
(e) quicklime
(d) slaked lime
Ans. (c)
10. Bleaching powder is
(a) CaO2C1
(b) CaOCl2
(c) CaC1O2
(d) CaC12 + O2
Ans. (b)
11. Baking powder contains Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate and
(a) tartaric acid
(b) sodium carbonate
(c) calcium chloride
(d) acetic acid
Ans. (a)
12. Plaster of Paris is obtained by heating
(a) gypsum
(b) limestone
(c) sodium carbonate
(d) calcium sulphate
Ans. (a)
14. The common name of sodium bicarbonate is
(a) lime
(b) baking powder
(c) baking soda
(d) washing soda
Ans. (b)
14. Soda Acid for extinguisher contains
(a) sodium carbonate and nitric acid
(b) sodium hydrogen carbonate and sulphuric acid
(c) sodium carbonate and carbonic acid
(d) sodium chloride and sulphuric acid
Ans. (b)
15. Efflorescence is shown by
(a) bleaching powder
(b) baking soda
(c) washing soda
(d) plaster of Paris
Ans. (c)
16. Slaked lime reacts with chlorine to give
(a) baking soda
(b) washing soda
(c) bleaching powder
(d) cement
Ans. (c)
17. The main constituent of cement is
(a) Si02
(b) CaO
(c) CaSO4
(d) Al203
Ans. (a)
18. Sodium Carbonate is prepared on large scale by
(a) Solvay’s process
(b) Beckmann’s plants
(c) Hesenclover plant
(d) adding water to lime
Ans. (a)
19. Name a compound which hardens on wetting with water.
(a) Calcium sulphate decahydrate
(b) Calcium sulphur hemihydrates
(c) Calcium sulphate
(d) Hydrated calcium sulphate
Ans. (b)
20. The real bleaching agent present in bleaching powder is
(a) chlorine
(b) oxygen
(c) CaO
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a)
(a) mortar
(b) concrete
(c) slurry
(d) hardner
Ans. (b)
2. RCC is
(a) the concrete having an iron framework inside it as a support
(b) the crushed cement in which more gravel is added
(c) prepared by adding calcium chloride to the limestone and calcium silicate
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a)
3. The process of making soap by the hydrolysis of fats and oils with alkalis is called
(a) hydrolysis
(b) saponification
(c) esterification
(d) none of the above
Ans. (b)
4. The soap can be hardened by
(a) adding sodium carbonate or sodium silicate during its manufacture
(b) adding sodium chloride
(c) adding potassium hydroxide
(d) adding animal fat and coconut oil
Ans. (a)
5. Endoscope is made up of
(a) glass wool
(b) optical fibres
(c) optical glass
(d) lead crystal glass
Ans. (b)
6. The plastics which soften upon being heated but regains all its original properties on
cooling are known as
(a) thermoplastics
(b) thermosetting plastics
(c) thermoelastic
(d) cellulose
Ans. (a)
7. Which of the following is not a thermoplastic polymer?
(a) Nylon
(b) PVC
(c) Polythene
(d) Bakelite
Ans. (d)
8. Match the following:
I II
(A) Heat resistant 1. Used as insulating
Glass material in oven
(B) Glass wool 2. Useful as sun shield
(C) Laminated glass 3. Borosilicate glass
(D) Photochromatic 4, Used in bullet proof
glass screens
A B C D
(a) 2 4 1 3
(b) 3 1 4 3
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 3 2 1 4
Ans. (c)
9. Limestone on heating gives
(a) washing soda
(b) plaster of Paris
(e) quicklime
(d) slaked lime
Ans. (c)
10. Bleaching powder is
(a) CaO2C1
(b) CaOCl2
(c) CaC1O2
(d) CaC12 + O2
Ans. (b)
11. Baking powder contains Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate and
(a) tartaric acid
(b) sodium carbonate
(c) calcium chloride
(d) acetic acid
Ans. (a)
12. Plaster of Paris is obtained by heating
(a) gypsum
(b) limestone
(c) sodium carbonate
(d) calcium sulphate
Ans. (a)
14. The common name of sodium bicarbonate is
(a) lime
(b) baking powder
(c) baking soda
(d) washing soda
Ans. (b)
14. Soda Acid for extinguisher contains
(a) sodium carbonate and nitric acid
(b) sodium hydrogen carbonate and sulphuric acid
(c) sodium carbonate and carbonic acid
(d) sodium chloride and sulphuric acid
Ans. (b)
15. Efflorescence is shown by
(a) bleaching powder
(b) baking soda
(c) washing soda
(d) plaster of Paris
Ans. (c)
16. Slaked lime reacts with chlorine to give
(a) baking soda
(b) washing soda
(c) bleaching powder
(d) cement
Ans. (c)
17. The main constituent of cement is
(a) Si02
(b) CaO
(c) CaSO4
(d) Al203
Ans. (a)
18. Sodium Carbonate is prepared on large scale by
(a) Solvay’s process
(b) Beckmann’s plants
(c) Hesenclover plant
(d) adding water to lime
Ans. (a)
19. Name a compound which hardens on wetting with water.
(a) Calcium sulphate decahydrate
(b) Calcium sulphur hemihydrates
(c) Calcium sulphate
(d) Hydrated calcium sulphate
Ans. (b)
20. The real bleaching agent present in bleaching powder is
(a) chlorine
(b) oxygen
(c) CaO
(d) none of the above
Ans. (a)
CIVIL ENGINEERING PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Static formulae 1. To estimate allowable load for permissible settlement for pile
B. Dynamic formulae 2. To separate point bearing and friction bearing capacities of a
Pile
C. Static pile load test 3. To estimate allowable load for driven piles in granular soils
D. Cyclic pile load test 4. to estimate allowable load for bored piles in clays
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 2 4 1
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 4 2 3 1
Ans. (b)
2. Consider the following statements:
1. Piles are provided in groups, which are connected together by a pile cap. The structure rests on top of the pile cap. The pile cap is situated below the ground level.
2. For situations where pile is subjected to upward pull, pedestal piles or under reamed piles are more suitable type of foundations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (c)
3. In comparison to Atterberg limits of normal soils, the expansive soils have which of the following?
1. More liquid limit
2. Less plastic limit
3. Less shrinkage limit
4. More volumetric shrinkage
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and4 only
Ans. (a)
4. Consider the following statements:
On addition of lime to swelling soils,
1. their liquid limit increases
2. their plastic limit increases
3. their shrinkage limit increases
4. their swelling potential decreases
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) l, 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
5. Consider the following statements about the under-reamed pile in swelling soils:
On addition of lime to swelling soils,
1. Its bulb provides anchor against movement due to volume changes of soil.
2. It is a driven pile.
3. Its bulb diameter is 2.5 times its shaft diameter.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans. (d)
6. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given, below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Foundation) (Demanding Situation)
A. Under-reamed piles 1. To restrict settlement of soft clays/silts
B. Floating rafts 2. To transfer the moment in between two adjacent footings
C. Combined footing 3. To restrict damages due to volume changes of swelling soils
D. Strap footing 4. When columns are very close to the property line
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 2 4 1
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 4 2 3 1
(d) 3 1 4 2
Ans. (d)
7. A differential free swell test on a soil gives a value of differential free swell of 40%. What is the degree of swelling?
(a) Low
(b) Medium
(c) High
(d) Very high
Ans. (c)
8. Which factors influence the bearing capacity of a purely cohesionless soil?
1. Relative density of soil
2. Width and depth of footing
3. Unit weight of soil
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
9. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Field Test) (Suitability)
A. Plate load Test 1. To estimate bearing capacity of granular soil
B. Standard penetration test 2. To estimate ii situ strength of soft clay
C. Vane shear test 3. To identify silt from clay
D. Dilatancy test 4. To estimate bearing capacity for permissible
settlement, in clays
Code:
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 3 4 1
Ans. (c)
10. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Test) (Utility)
A. Field Density test 1. Stress deformation characteristics
B. Plate load test 2. Compaction characteristics
C. C.B.R. test 3. Design of pavement
4. Safe load bearing capacity of soil
Code:
A B C
(a) 2 4 1
(b) 4 2 1
(c) 4 2 3
(d) 2 4 3
Ans. (d)
11. Which of the following can be ud as a map substitute?
(a) Terrestrial photographs
(b) Vertical aerial photographs
(c) Oblique aerial photographs
(d) Vertical aerial photo-mosaics
Ans. (b)
12. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the
lists:
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Visual Inter pretation system 1. Creation of data bank of multi information for a
project area
B. Geographical Information System 2. Visual identification of objects from image
characteristics
C. National Remote Sensing Agency 3. Computer classification of digital image data
D. Supervised Image Classification 4. Supplier of aerial and satellite based remote
sensing data products in India
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 1 4 2 3
Ans. (b)
13. Which one of the following is not strictly a method of remote sensing?
(a) Thermal and multi-spectral scanning
(b) Microwave sensing
(c) Earth resource satellite
(d) Stereoscopy
Ans. (c)
14. Consider the following bituminous surfacing:
1. SDBM
2. PMC
3. A.C.
4. S.D.
5. Mastic Asphalt (M.A.)
Which one of the following, is thee correct sequence in, increasing order with respect to their performance and wearing qualities?
(a) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5
(b) 2, 4, 1, 5, 3
(c) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5
(d) 1, 4, 3, 2, 5
Ans. (c)
15. Consider the following statements with reference to Water Bound Macadam (WBM) and Wet Mix Macadam (WMM):
1. WBM is a road mix and WMM is a plant mix.
2. WBM usually has plastic filler, while WMM has non-plastic filler.
3. WBM is a modern road mix and WMM is a traditional road mix.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 only
(d) 2 only
Ans. (a)
16. A scale of 1 inch = 50 ft. is mentioned on an old mp. What is the corresponding equivalent scale?
(a) 1 cm = 5 m
(b) 4cm = 6m
(c) lcm = l0m
(d) 1 cm = 12 m
Ans. (b)
17. The Whole Circle Bearings of lines AB and BC are 30°15’. What is the included angle ABC between the lines AB and BC?
(a) 229° 45´
(b) 89° 45´
(c) 269° 45´
(d) 90o15´
Ans. (b)
18. What is Angle ABC if B of lint AB is 40o and BB of line BC is 280°?
(a) 90°
(b) 120o
(c) 240°
(d) 20°
19. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Change point is a point denoting shifting of level
(b) For levelling work both centering and levelling of a dumpy level are prerequisite
(c) Bench Mark is a point whose R.L. is always known
(d) None of these
Ans. (d)
20. Consider the following statements about the characteristics of contours:
1. Closed contour lines with higher values inside shown a lake.
2. Contour is an imaginary line joining points of equal elevations.
3. Closely spaced contours indicate steep slope.
4. Contour lines can cross each other in case an overhanging cliff.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (a)
21. In modal choice studies which one of the following factors influences the shape of
diversion curves?
(a) Trip purpose
(b) Trip length
(c) Income
(d) Residential density
Ans. (a)
22. Which one, of the following methods of tunnelling is employed if the strata is subaqueous?
(a) Shield tunneling
(b) Drift system
(c) Liner plate method
(d) Pilot tunnel method
Ans. (c)
23. Weishbauh Triangle method may be used for which one of the following?
(a) To carry out surface alignment of a tunnel
(b) To transfer levels underground for a tunnel
(c) To connect surface and underground tunnel surveys
(d) To connect two ends of an underground tunnel
Ans. (d)
24. How can additional access, quick removal of muck and natural ventilation in long tunnne1s be achieved?
(a) By providing jumbos and pumps
(b) By providing scaffolding and linear plates
(c) By providing adits and shafts
(d) By providing pilot tunnels and well points
Ans. (c)
25. The ‘track modulus’ is an index of measure of which of the following?
(a) Resistance due to fiction
(b) Resistance due to hear
(c Resistance due to deformation
(d) Resistance due to rolling
Ans. (c)
26. IRC code No. 37-1985 deals with which one of the following?
(a) Design of rigid pavements, taking ESWL and CI3R into account
(b) Design of rigid pavements, taking in axle load and CBR into account
(c) Design of flexible pavement, taking ESWL and CBR into account
(d) Design of flexible pavement taking cumulative axle loads and CBR into account
Ans. (d)
27. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Traffic Volume 1. Number of vehicles occupying a unit length of road at
a given instant of time
B. Traffic Density 2. Number of vehicles passing a given point on’ road in a
given unit of time in a given direction
C. Traffic Regulations 3 . Where all converging vehicles are forced to move in
one direction around a large central traffic island
(D) Rotary Intersection 4. Rules covering all aspects of control of vehicle, drivers
and fall other road users
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 1 4 2 3
Ans. (c)
28. Which of the following factors are not strictly related to design of traffic rotary intersections?
1. Radius of central island
2. Weaving length’
3. Ramps and interchanges
4. Acceleration lanes
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans. (d)
29. In urban transportation planning, the ‘Modal Split’ is the process of which one of the following?
(a) Staggering of working hours
(b) Segregation of fast and low modes
(c) Separation of traffic streams by flyovers
(d) Deciding the choice for a mode
30. What is the minimum turning radius for a passenger ship?
(a) 2 x ship length
(b) 3 x ship length -
(c) (1.5 x ship length) + water depth
(d) (2 x ship length) + (1.5 draft)
Ans. (a)
31. Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
1. Vishakhapatnam: Semi-natural harbor Plymouth
2. Paradip and Mangalore: Lagoon harbour
3. New York: Natural harbour
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 Only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
32. Echo-sounding machine is used for which of the following?
1. Locating objects. On sea-shore
2. Measuring sea-surface levels
3. Determining depth of sea-bed below sea surface
4. Locating sunken objects below sea surface Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans. (d)
33. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Components) (Function)
A. Keel and Bilge blocks 1. Impact absorbers of quay walls
B. Capstons and Bolards 2. Floating indicators
C. Fenders 3.Supports for ships in dry docks
D. Buoys 4. Anchorage devices for ships
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 4 1 2
(b) 4 3 1 2
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 4 2 1
Ans. (a)
34. Mean sea level at Indian posts and harbours has generally been established based on the analysis of tidal sea water level fluctuations over which period?
(a) 10 years
(b) 16 years
(c) 19 years
(d) 25 years
Ans. (c)
35. Which of the following factors help in ensuring track modulus, in a railway track?
(a) Gauge and formation width
(b) Track. materials and sleeper density
(c) Degree of curvature and super elevation
(d) Length of rail and flange width
Ans. (b)
36. What is the hauling capacity of a railway locomotive having 4 pairs of driving wheels, carrying an axle load of 24 tonnes each? (Assume 0.166 as the coefficient of friction)
(a) 16.5 tonnes
(b) 160 tonnes
(c) 15.5 tonnes
(d) 17.0 tonnes
Ans. (b)
37. The vertical weal on tongue rail Should not exceed which one of the following?
(a) 6 mm
(b) 10 mm
(c) 12 mm
(d) 15 mm
Ans. (b)
38. Which of the following are related to maintenance of railway track?
1. Jim crow and gauge bar
2. Through packing and boxing
3. Buffer stop and sand hump
4. Creep adjustment
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
39. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List- I List-II
(Harbour Structure) (Purpose)
A. Dolphins 1. To Protect the beach or retained earth
B. Groynes 2. To cushion to absorb shock of ship during loading
and unloading
C. Fenders 3. Mooring structure in combination with loading
Platform
D. Slipways 4. Repairing and building ship
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 3 1 2 4
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 4 2 1
Ans. (b)
40. The shape number in the case of pumps refers to which one of the following?
(a) Ratio of sizes of suction pipe and delivery pipe
(b) Ratio of diameter and thickness of impeller
(c) Non dimensional farm of specific speed
(d) Ratio of angle at the inlet to the blade angle at the exit
Ans. (c)
41. Consider the following statements:
Due to aging of pipes in a pie network
(1) the roughness increases linearly with time
(2) the pipes get rusted and bent
(3) the pipes become smoother with time
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 only
Ans. (d)
42. While using Darcy-Weisbach equation for estimating head loss in a pipe flow, the friction factor was misjudged by + 0%. For this case, error in estimating discharge is:
(a) + 10%
(b) + 40%
(c) - 40%
(d) - 10%
Ans. (d)
43. A 4 hr storm had 4 cm of rainfall and the resulting direct runoff was 2.0 cm. If the
Φ-index remains at the same value, the runoff due to 10 cm of rainfall in 8 hrs in the
catchments is
(a) 6.0 cm
(b) 7.5 cm
(c) 2.3 cm
(d) 2.8 cm
Ans. (a)
44. Which of the following statements is/are correct? Lining of irrigation canals has necessarily to be carried out in the reaches where the channel passes through
(1) 1 and soil
(2) coarse aggregate soil
(3) clay soil
(4) fine silt and clay
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 3 and 4only
Ans. (c)
45. The orientation of runway is decided by which factors?
(1) Maximum wind coverage and least cross winds
(2) Landing characteristics of aircr4ft
(3) Scope for future expansion
(4) Obstruction-free approaches
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
46. The size of hangar in an airport is guided by which of the following
(a) Speed and direction of wind and visibility
(b) Weight of aircraft and turning needs
(c) The fuelling capacity and storage space
(d) The length, wingspan and height of aircraft
Ans. (d)
47. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Component) (Design Feature)
A. Taxiways 1. Large span structures
B. Control tower 2. Visibility all round and sound-proof
C. Hagnar 3. Turning radius
D. Apron 4. Waiting capacity for aircraft
Code:
A B C D
(a) 1 4 3 2
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 4 1 2
Ans. (b)
48. Consider the following statements
(1) Fluids of low viscosity are all irrotational
(2) Rotation of the fluid is always associated with shear stress
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (b)
49. Consider the following statements
(1) Hydraulically most efficient channel section for an open channel flow will carry maximum discharge for a given area of cross section
(2) For a given cross sectional area hydraulic radius is maximum when the wetted perimeter is minimum
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (c)
50. Flamsteed gave numbers to stars observed by him in each constellation according to
their
(a) Brilliance
(b) Altitudes
(c) Co-declinations
(d) Right ascensions
Ans. (d)
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Static formulae 1. To estimate allowable load for permissible settlement for pile
B. Dynamic formulae 2. To separate point bearing and friction bearing capacities of a
Pile
C. Static pile load test 3. To estimate allowable load for driven piles in granular soils
D. Cyclic pile load test 4. to estimate allowable load for bored piles in clays
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 2 4 1
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 4 2 3 1
Ans. (b)
2. Consider the following statements:
1. Piles are provided in groups, which are connected together by a pile cap. The structure rests on top of the pile cap. The pile cap is situated below the ground level.
2. For situations where pile is subjected to upward pull, pedestal piles or under reamed piles are more suitable type of foundations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (c)
3. In comparison to Atterberg limits of normal soils, the expansive soils have which of the following?
1. More liquid limit
2. Less plastic limit
3. Less shrinkage limit
4. More volumetric shrinkage
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and4 only
Ans. (a)
4. Consider the following statements:
On addition of lime to swelling soils,
1. their liquid limit increases
2. their plastic limit increases
3. their shrinkage limit increases
4. their swelling potential decreases
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) l, 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
5. Consider the following statements about the under-reamed pile in swelling soils:
On addition of lime to swelling soils,
1. Its bulb provides anchor against movement due to volume changes of soil.
2. It is a driven pile.
3. Its bulb diameter is 2.5 times its shaft diameter.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans. (d)
6. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given, below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Foundation) (Demanding Situation)
A. Under-reamed piles 1. To restrict settlement of soft clays/silts
B. Floating rafts 2. To transfer the moment in between two adjacent footings
C. Combined footing 3. To restrict damages due to volume changes of swelling soils
D. Strap footing 4. When columns are very close to the property line
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 2 4 1
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 4 2 3 1
(d) 3 1 4 2
Ans. (d)
7. A differential free swell test on a soil gives a value of differential free swell of 40%. What is the degree of swelling?
(a) Low
(b) Medium
(c) High
(d) Very high
Ans. (c)
8. Which factors influence the bearing capacity of a purely cohesionless soil?
1. Relative density of soil
2. Width and depth of footing
3. Unit weight of soil
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
9. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Field Test) (Suitability)
A. Plate load Test 1. To estimate bearing capacity of granular soil
B. Standard penetration test 2. To estimate ii situ strength of soft clay
C. Vane shear test 3. To identify silt from clay
D. Dilatancy test 4. To estimate bearing capacity for permissible
settlement, in clays
Code:
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 3 4 1
Ans. (c)
10. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Test) (Utility)
A. Field Density test 1. Stress deformation characteristics
B. Plate load test 2. Compaction characteristics
C. C.B.R. test 3. Design of pavement
4. Safe load bearing capacity of soil
Code:
A B C
(a) 2 4 1
(b) 4 2 1
(c) 4 2 3
(d) 2 4 3
Ans. (d)
11. Which of the following can be ud as a map substitute?
(a) Terrestrial photographs
(b) Vertical aerial photographs
(c) Oblique aerial photographs
(d) Vertical aerial photo-mosaics
Ans. (b)
12. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the
lists:
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Visual Inter pretation system 1. Creation of data bank of multi information for a
project area
B. Geographical Information System 2. Visual identification of objects from image
characteristics
C. National Remote Sensing Agency 3. Computer classification of digital image data
D. Supervised Image Classification 4. Supplier of aerial and satellite based remote
sensing data products in India
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 1 4 2 3
Ans. (b)
13. Which one of the following is not strictly a method of remote sensing?
(a) Thermal and multi-spectral scanning
(b) Microwave sensing
(c) Earth resource satellite
(d) Stereoscopy
Ans. (c)
14. Consider the following bituminous surfacing:
1. SDBM
2. PMC
3. A.C.
4. S.D.
5. Mastic Asphalt (M.A.)
Which one of the following, is thee correct sequence in, increasing order with respect to their performance and wearing qualities?
(a) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5
(b) 2, 4, 1, 5, 3
(c) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5
(d) 1, 4, 3, 2, 5
Ans. (c)
15. Consider the following statements with reference to Water Bound Macadam (WBM) and Wet Mix Macadam (WMM):
1. WBM is a road mix and WMM is a plant mix.
2. WBM usually has plastic filler, while WMM has non-plastic filler.
3. WBM is a modern road mix and WMM is a traditional road mix.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 only
(d) 2 only
Ans. (a)
16. A scale of 1 inch = 50 ft. is mentioned on an old mp. What is the corresponding equivalent scale?
(a) 1 cm = 5 m
(b) 4cm = 6m
(c) lcm = l0m
(d) 1 cm = 12 m
Ans. (b)
17. The Whole Circle Bearings of lines AB and BC are 30°15’. What is the included angle ABC between the lines AB and BC?
(a) 229° 45´
(b) 89° 45´
(c) 269° 45´
(d) 90o15´
Ans. (b)
18. What is Angle ABC if B of lint AB is 40o and BB of line BC is 280°?
(a) 90°
(b) 120o
(c) 240°
(d) 20°
19. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Change point is a point denoting shifting of level
(b) For levelling work both centering and levelling of a dumpy level are prerequisite
(c) Bench Mark is a point whose R.L. is always known
(d) None of these
Ans. (d)
20. Consider the following statements about the characteristics of contours:
1. Closed contour lines with higher values inside shown a lake.
2. Contour is an imaginary line joining points of equal elevations.
3. Closely spaced contours indicate steep slope.
4. Contour lines can cross each other in case an overhanging cliff.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (a)
21. In modal choice studies which one of the following factors influences the shape of
diversion curves?
(a) Trip purpose
(b) Trip length
(c) Income
(d) Residential density
Ans. (a)
22. Which one, of the following methods of tunnelling is employed if the strata is subaqueous?
(a) Shield tunneling
(b) Drift system
(c) Liner plate method
(d) Pilot tunnel method
Ans. (c)
23. Weishbauh Triangle method may be used for which one of the following?
(a) To carry out surface alignment of a tunnel
(b) To transfer levels underground for a tunnel
(c) To connect surface and underground tunnel surveys
(d) To connect two ends of an underground tunnel
Ans. (d)
24. How can additional access, quick removal of muck and natural ventilation in long tunnne1s be achieved?
(a) By providing jumbos and pumps
(b) By providing scaffolding and linear plates
(c) By providing adits and shafts
(d) By providing pilot tunnels and well points
Ans. (c)
25. The ‘track modulus’ is an index of measure of which of the following?
(a) Resistance due to fiction
(b) Resistance due to hear
(c Resistance due to deformation
(d) Resistance due to rolling
Ans. (c)
26. IRC code No. 37-1985 deals with which one of the following?
(a) Design of rigid pavements, taking ESWL and CI3R into account
(b) Design of rigid pavements, taking in axle load and CBR into account
(c) Design of flexible pavement, taking ESWL and CBR into account
(d) Design of flexible pavement taking cumulative axle loads and CBR into account
Ans. (d)
27. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Method) (Suitability)
A. Traffic Volume 1. Number of vehicles occupying a unit length of road at
a given instant of time
B. Traffic Density 2. Number of vehicles passing a given point on’ road in a
given unit of time in a given direction
C. Traffic Regulations 3 . Where all converging vehicles are forced to move in
one direction around a large central traffic island
(D) Rotary Intersection 4. Rules covering all aspects of control of vehicle, drivers
and fall other road users
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 1 4 2 3
Ans. (c)
28. Which of the following factors are not strictly related to design of traffic rotary intersections?
1. Radius of central island
2. Weaving length’
3. Ramps and interchanges
4. Acceleration lanes
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans. (d)
29. In urban transportation planning, the ‘Modal Split’ is the process of which one of the following?
(a) Staggering of working hours
(b) Segregation of fast and low modes
(c) Separation of traffic streams by flyovers
(d) Deciding the choice for a mode
30. What is the minimum turning radius for a passenger ship?
(a) 2 x ship length
(b) 3 x ship length -
(c) (1.5 x ship length) + water depth
(d) (2 x ship length) + (1.5 draft)
Ans. (a)
31. Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
1. Vishakhapatnam: Semi-natural harbor Plymouth
2. Paradip and Mangalore: Lagoon harbour
3. New York: Natural harbour
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 Only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
32. Echo-sounding machine is used for which of the following?
1. Locating objects. On sea-shore
2. Measuring sea-surface levels
3. Determining depth of sea-bed below sea surface
4. Locating sunken objects below sea surface Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans. (d)
33. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Components) (Function)
A. Keel and Bilge blocks 1. Impact absorbers of quay walls
B. Capstons and Bolards 2. Floating indicators
C. Fenders 3.Supports for ships in dry docks
D. Buoys 4. Anchorage devices for ships
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 4 1 2
(b) 4 3 1 2
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 4 2 1
Ans. (a)
34. Mean sea level at Indian posts and harbours has generally been established based on the analysis of tidal sea water level fluctuations over which period?
(a) 10 years
(b) 16 years
(c) 19 years
(d) 25 years
Ans. (c)
35. Which of the following factors help in ensuring track modulus, in a railway track?
(a) Gauge and formation width
(b) Track. materials and sleeper density
(c) Degree of curvature and super elevation
(d) Length of rail and flange width
Ans. (b)
36. What is the hauling capacity of a railway locomotive having 4 pairs of driving wheels, carrying an axle load of 24 tonnes each? (Assume 0.166 as the coefficient of friction)
(a) 16.5 tonnes
(b) 160 tonnes
(c) 15.5 tonnes
(d) 17.0 tonnes
Ans. (b)
37. The vertical weal on tongue rail Should not exceed which one of the following?
(a) 6 mm
(b) 10 mm
(c) 12 mm
(d) 15 mm
Ans. (b)
38. Which of the following are related to maintenance of railway track?
1. Jim crow and gauge bar
2. Through packing and boxing
3. Buffer stop and sand hump
4. Creep adjustment
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
39. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List- I List-II
(Harbour Structure) (Purpose)
A. Dolphins 1. To Protect the beach or retained earth
B. Groynes 2. To cushion to absorb shock of ship during loading
and unloading
C. Fenders 3. Mooring structure in combination with loading
Platform
D. Slipways 4. Repairing and building ship
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 3 1 2 4
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 4 2 1
Ans. (b)
40. The shape number in the case of pumps refers to which one of the following?
(a) Ratio of sizes of suction pipe and delivery pipe
(b) Ratio of diameter and thickness of impeller
(c) Non dimensional farm of specific speed
(d) Ratio of angle at the inlet to the blade angle at the exit
Ans. (c)
41. Consider the following statements:
Due to aging of pipes in a pie network
(1) the roughness increases linearly with time
(2) the pipes get rusted and bent
(3) the pipes become smoother with time
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 only
Ans. (d)
42. While using Darcy-Weisbach equation for estimating head loss in a pipe flow, the friction factor was misjudged by + 0%. For this case, error in estimating discharge is:
(a) + 10%
(b) + 40%
(c) - 40%
(d) - 10%
Ans. (d)
43. A 4 hr storm had 4 cm of rainfall and the resulting direct runoff was 2.0 cm. If the
Φ-index remains at the same value, the runoff due to 10 cm of rainfall in 8 hrs in the
catchments is
(a) 6.0 cm
(b) 7.5 cm
(c) 2.3 cm
(d) 2.8 cm
Ans. (a)
44. Which of the following statements is/are correct? Lining of irrigation canals has necessarily to be carried out in the reaches where the channel passes through
(1) 1 and soil
(2) coarse aggregate soil
(3) clay soil
(4) fine silt and clay
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 3 and 4only
Ans. (c)
45. The orientation of runway is decided by which factors?
(1) Maximum wind coverage and least cross winds
(2) Landing characteristics of aircr4ft
(3) Scope for future expansion
(4) Obstruction-free approaches
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
46. The size of hangar in an airport is guided by which of the following
(a) Speed and direction of wind and visibility
(b) Weight of aircraft and turning needs
(c) The fuelling capacity and storage space
(d) The length, wingspan and height of aircraft
Ans. (d)
47. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Component) (Design Feature)
A. Taxiways 1. Large span structures
B. Control tower 2. Visibility all round and sound-proof
C. Hagnar 3. Turning radius
D. Apron 4. Waiting capacity for aircraft
Code:
A B C D
(a) 1 4 3 2
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 4 1 2
Ans. (b)
48. Consider the following statements
(1) Fluids of low viscosity are all irrotational
(2) Rotation of the fluid is always associated with shear stress
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (b)
49. Consider the following statements
(1) Hydraulically most efficient channel section for an open channel flow will carry maximum discharge for a given area of cross section
(2) For a given cross sectional area hydraulic radius is maximum when the wetted perimeter is minimum
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (c)
50. Flamsteed gave numbers to stars observed by him in each constellation according to
their
(a) Brilliance
(b) Altitudes
(c) Co-declinations
(d) Right ascensions
Ans. (d)
CIVIL ENGINEERING PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. Consider the following statements:
The use of super plasticizers as admixture
1. Increases compressive strength of concrete
2. Permits lower water-cement ratio, thereby strength is increased
3. Reduces the setting time of concrete
4. Permits lower cement content, thereby strength is increased
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I and 3 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1,3and4only
(d) 2 only
Ans. (d)
2. Consider the following statements:
Curing of concrete is necessary because
1. Concrete needs more water for chemical reaction
2. It is necessary to protect the water initially mixed in concrete from being lost during evaporation
3. Penetration of surrounding water increases the strength of concrete
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 3 only
Ans. (c)
3. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
List-I List-II
A. Absorption and surface moisture in 1. Interferes with hydration of cement
aggregates
B. Deleterious material 2. Improves work-ability of mix
C. Grading of aggregate 3. Ensures durability of all types of structures
D. Chemical stability 4. Affects the mix proportions
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 1 2 4
(b) 4 2 1 3
(c) 3 2 1 4
(d) 4 1 2 3
Ans. (d)
4. Why are bricks soaked in water before using in brick masonry?
(a) For removing dust
(b) For reducing air voids
(c) For preventing depletion of moisture from mortar
(d) For reducing efflorescence
Ans. (c)
5. Which type of brick masonry bond is provided for heavy loads on masonry?
(a) English bond
(b) Zigzag bond
(c) Single Flemish bond
(d) Double Flemish bond
Ans. (a)
6. Consider the following, types of cements:
1. Portland pulverized fuel ash cement
2. High alumina cement.
3. Ordinary Portland cement
4. Rapid hardening cement
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the above cement in terms of their
increasing rate of strength gain?
(a) 2-3-4-1
(b) 1-3-4-2
(c) 2-1-3-4
(d) 3-1-2-4
Ans. (c)
7. Ultimate strength of cement is influenced by which one of the following?
(a) Tricalcium silicate
(b) Dicalcium silicate
(c) Tricalcium aluminate
(d) Tetracalcium alumino ferrite
Ans. (b)
8. Why is lime added to cement slurry for the topcoat of plastering?
(a) To improve the strength of plaster
(b) To stiffen the plaster
(c) To smoothen the plaster for ease of spread
(d) To make the plaster non-shrinkable
Ans. (d)
9. What is the number of plastic hinges which will cause the overall total collapse of a structure?
(a) One more than the order of statical indeterminacy
(b) Equal to order of statical indeterminacy
(c) One less than the order of statical indeterminacy
(d) Not determinable
Ans. (a)
10. What is/are the use(s) of influence lines?
(a) To study the effect of moving loads on the structure
(b) To calculate the value of stress function with the critical load condition
(c) To find the position of live load for a maximum value of particular stress function
(d) Towards all the above purposes
Ans. (d)
11. What is the variation of influence line for stress function in a statically determinate structure?
(a) Parabolic
(b) Bilinear
(c) Linear
(d) Uniformly rectangular
Ans. (c)
12. What is the maximum permissible longitudinal pitch in staggered riveted compression joints?
(a) 500 mm
(b) 400mm
(c) 300mm
(d) 100mm
Ans. (c)
13. A concentrated load W moves on the span of a three-hinged arch. The horizontal thrust at the supports is maximum when the load is at which one of the following?
(a) The springing
(b) One-sixth of the span from one end
(c) Quarter span
(d) The crown
Ans. (d)
14. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
In a gusseted base, when the end of the column is machined for complete bearing on the base plate, the axial load is assumed to be transferred to the base plate
(a) Fully by direct bearing
(b) Fully through the fastenings
(c) 50% by direct bearing and 50% through fastenings
(d) 75% by direct bearing and 25% through fastenings
Ans. (c)
15. A tractor-trailer assembly has a gross weight of 25 tonnes. When moving over a level road, its rolling resistance is 42 kg per tonne. It is moved up a road of 5% grade. What is the required tractive effort?
(a) 1050.5kg
(b) 1060.5kg
(c) 1085kg
(d) 1102.5kg
Ans. (d)
16. Which one of the following shovel excavators is considered most efficient in loading
carriers?
(a) Dipper shovel
(b) Dragline
(c) Backhoe
(d) Clamshell
Ans. (c)
17. Bottom-dump wagons are suitable for handling which of the following?
(a) Wet sticky clay
(b) Sand and gravel
(c) Quarry rocks
(d) Any type of material
Ans. (b)
18. Vibratory rollers are more useful for compacting which of the following?
(a) Sandy soils
(b) Salty soils
(c) Clayey soils
(d) Mixed soils
Ans. (a)
19. The displacement method is also referred to as which one of the following?
(a) Minimum strain energy method
(b) Maxwell-Mohr method
(c) Consistent deformation method
(d) Slope-deflection method
Ans. (d)
20. A beam .carries a uniformly distributed load throughout its length. In which of the following configurations will the strain energy be maximum?
(a) Cantilever
(b) Simply supported beam
(c) Propped cantilever
(d) Fixed beam
Ans. (a)
21. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) In slope-deflection method, the forces are taken as unknowns
(b) In slope-deflection method, the joint rotations are taken as unknowns
(c) Slope-deflection method is not applicable for beams and frames having-settlement at supports
(d) Slope-deflection method is also known as force method
Ans. (b)
22. When the effect of wind or earthquake load is considered in the design of rivets and bolts for steel structures, by what percentage the permissible stresses may be exceeded?
(a) 15%
(b) 25%
(c) 33.33%
(d) 50%
Ans. (c)
23. The working range of a crane is limited horizontally for maximum lift only by
(a) Boom length
(b) Length of hoist cable
(c) Length of jib
(d) Counter weight
Ans. (c)
24. What is a tendon profile, in which the eccentricity is proportional to the bending moment caused by any loading on a rigidly supported indeterminate structure, at all cross-sections?
(a) Cable profile
(b) Resultant profile
(c) Concordant profile
(d) Reduced profile
Ans. (c)
25. When power shovels are operated under different site conditions (in terms of material handled), what is the correct sequence in the increasing order of the output for the following materials?
1. Well-blasted rock
2. Hard and tough clay
3. Poorly blasted rock
4. Moist loam or sane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Code:
(a) 1-2-3-4
(b) 1-4-3-2
(c) 4-2-3-1
(d) 4-3-1-2
Ans. (c)
26. For three-dimensional movement of a weight, which one of the following is most suitable?
(a) Chain hoist
(b) Winch
(c) Crane
(d) Jack
Ans. (c)
27. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
List-I (Crane) List-II (Suitable for)
A. Tower crane 1. Hydraulic structures
B. Floating crane 2. High industrial plant
C. Mobile crane 3. Longitudinal and lateral movements of load
D. Gantry crane 4. Railway electrification
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 2 4 1 3
(d) 3 1 4 2
Ans. (a)
28. How are concrete mixers specified?
(a) By the number of cement bags used in a batch
(b) By the nominal volume of concrete that can be mixed in a batch
(c) By the volume of water used
(d) By the volume of aggregate used
Ans. (b)
29. What is the minimum width of roadway for a six-lane high-level bridge constructed for the use of road traffic only?
(a) 21.5 m
(b) 22.5 m
(c) 24.0 m
(d) 25.5 m
Ans. (a)
30. Consider the following statements related to interchanges:
1. In diamond interchange there is the possibility of illegal wrong-way turns.
2. Diamond interchange is far superior to cloverleaf design.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither I nor 2
Ans. (a)
31. If a road surface is adequately supperelevated on horizontal curve, which one of the following is the proper distribution of pressure on the vehicle wheels?
(a) Pressure on both outer and inner wheels is equal
(b) Pressure on inner wheels is more than the outer wheels
(c) Pressure on inner wheels is less than the outer wheels
(d) Pressure on front wheels is thrice the pressure on rear wheels
Ans. (a)
32. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Type of Construction) (Binder Content Generally Specified)
A: Bituminous macadam 1. 8—15%
B. Dense bituminous macadam 2. 3—15%
C. Bituminous concrete 3. 4—4.5%
D. Bitumen mastic 4. 4.5—6.0%
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 4 3 2 1
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 4 1 2 3
Ans. (c)
33. If the mean temperature of Sun’s surface is 6000 K and λm of its radiation is 0.5 μm, what is the mean temperature of Earth’s surface for which λm is 10.0 μm, according to Wien’s Displacement Law in Remote Sensing Concept?
(a) 25°C
(b) 28°C
(c) 27°C
(d) 30°C
Ans. (c)
34. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I (Term) List-II (Definition)
A. Apparent solar day 1. The time interval between two successive upper transits of the first point of Aries over the same meridian
B. Sidereal day 2. Time interval between two successive lower transits of the centre of the Sun across the same meridian
C. Tropical year 3. Time interval between two successive passages of the Sun over the meridian of any one of the fixed stars
D. Sidereal year 4. Time interval between two successive vernal equinoxes
Code:
A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 2 1 3 4
(d) 1 2 4 3
Ans. (b)
25. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
A streamlined body is one for which the
(a) Skin friction is zero.
(b) Thickness of the body is less than 1/100 of its length.
(c) Corners are rounded off.
(d) Separation occurs, if at all, at the farthest downstream part of the body
Ans. (d)
36. A flat plate with a sharp leading edge is placed along a free stream of fluid flow. Local Reynolds number at 3 cm from the leading edge is 105. What is the thickness of the boundary layer?
(a) 0.47mm
(b) 0.35 mm
(c) 0.23mm
(d) 0.12mm
Ans. (a)
37. During a flood in a stream of width 200 m (taken as rectangular section), the gauge reading was found to rise by 18 cm per hour. What would be the difference in discharges at two sections, each 250 m on either side of the gauge station?
(a) 10 m3/s less at downstream section
(b) 7.5 m3/s less at downstream section
(c) 5 m3/s less at downstream section
(d) 5 m3/s more at downstream section
Ans. (c)
38. If the stream function PHI = 3x3 — y3, what is the magnitude of velocity at point (2, 2)?
(a) 9
(b) 13
(c) 15
(d) 17
Ans. (d)
39. The weight of aggregate having specific gravity 2.65, completely filled into a cylinder of volume 0.003 m3 is 5.2 kg. What is the value of the angularity index of aggregate (approximately) as given by Murdock?
(a) 1
(b) 0.34
(c) 0.15
(d) 0.05
Ans. (b)
40. Which one of the following criteria is used for obtaining the value of modulus of subgrade reaction from plate bearing test data?
(a) Slope of pressure settlement graph
(b) Pressure corresponding to the settlement 1.25 mm
(c) Deflection corresponding to a pressure of 1.25 kg/ cm2
(d) Pressure corresponding to the settlement of 1.50 mm
Ans. (b)
The use of super plasticizers as admixture
1. Increases compressive strength of concrete
2. Permits lower water-cement ratio, thereby strength is increased
3. Reduces the setting time of concrete
4. Permits lower cement content, thereby strength is increased
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I and 3 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1,3and4only
(d) 2 only
Ans. (d)
2. Consider the following statements:
Curing of concrete is necessary because
1. Concrete needs more water for chemical reaction
2. It is necessary to protect the water initially mixed in concrete from being lost during evaporation
3. Penetration of surrounding water increases the strength of concrete
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 3 only
Ans. (c)
3. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
List-I List-II
A. Absorption and surface moisture in 1. Interferes with hydration of cement
aggregates
B. Deleterious material 2. Improves work-ability of mix
C. Grading of aggregate 3. Ensures durability of all types of structures
D. Chemical stability 4. Affects the mix proportions
Code:
A B C D
(a) 3 1 2 4
(b) 4 2 1 3
(c) 3 2 1 4
(d) 4 1 2 3
Ans. (d)
4. Why are bricks soaked in water before using in brick masonry?
(a) For removing dust
(b) For reducing air voids
(c) For preventing depletion of moisture from mortar
(d) For reducing efflorescence
Ans. (c)
5. Which type of brick masonry bond is provided for heavy loads on masonry?
(a) English bond
(b) Zigzag bond
(c) Single Flemish bond
(d) Double Flemish bond
Ans. (a)
6. Consider the following, types of cements:
1. Portland pulverized fuel ash cement
2. High alumina cement.
3. Ordinary Portland cement
4. Rapid hardening cement
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the above cement in terms of their
increasing rate of strength gain?
(a) 2-3-4-1
(b) 1-3-4-2
(c) 2-1-3-4
(d) 3-1-2-4
Ans. (c)
7. Ultimate strength of cement is influenced by which one of the following?
(a) Tricalcium silicate
(b) Dicalcium silicate
(c) Tricalcium aluminate
(d) Tetracalcium alumino ferrite
Ans. (b)
8. Why is lime added to cement slurry for the topcoat of plastering?
(a) To improve the strength of plaster
(b) To stiffen the plaster
(c) To smoothen the plaster for ease of spread
(d) To make the plaster non-shrinkable
Ans. (d)
9. What is the number of plastic hinges which will cause the overall total collapse of a structure?
(a) One more than the order of statical indeterminacy
(b) Equal to order of statical indeterminacy
(c) One less than the order of statical indeterminacy
(d) Not determinable
Ans. (a)
10. What is/are the use(s) of influence lines?
(a) To study the effect of moving loads on the structure
(b) To calculate the value of stress function with the critical load condition
(c) To find the position of live load for a maximum value of particular stress function
(d) Towards all the above purposes
Ans. (d)
11. What is the variation of influence line for stress function in a statically determinate structure?
(a) Parabolic
(b) Bilinear
(c) Linear
(d) Uniformly rectangular
Ans. (c)
12. What is the maximum permissible longitudinal pitch in staggered riveted compression joints?
(a) 500 mm
(b) 400mm
(c) 300mm
(d) 100mm
Ans. (c)
13. A concentrated load W moves on the span of a three-hinged arch. The horizontal thrust at the supports is maximum when the load is at which one of the following?
(a) The springing
(b) One-sixth of the span from one end
(c) Quarter span
(d) The crown
Ans. (d)
14. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
In a gusseted base, when the end of the column is machined for complete bearing on the base plate, the axial load is assumed to be transferred to the base plate
(a) Fully by direct bearing
(b) Fully through the fastenings
(c) 50% by direct bearing and 50% through fastenings
(d) 75% by direct bearing and 25% through fastenings
Ans. (c)
15. A tractor-trailer assembly has a gross weight of 25 tonnes. When moving over a level road, its rolling resistance is 42 kg per tonne. It is moved up a road of 5% grade. What is the required tractive effort?
(a) 1050.5kg
(b) 1060.5kg
(c) 1085kg
(d) 1102.5kg
Ans. (d)
16. Which one of the following shovel excavators is considered most efficient in loading
carriers?
(a) Dipper shovel
(b) Dragline
(c) Backhoe
(d) Clamshell
Ans. (c)
17. Bottom-dump wagons are suitable for handling which of the following?
(a) Wet sticky clay
(b) Sand and gravel
(c) Quarry rocks
(d) Any type of material
Ans. (b)
18. Vibratory rollers are more useful for compacting which of the following?
(a) Sandy soils
(b) Salty soils
(c) Clayey soils
(d) Mixed soils
Ans. (a)
19. The displacement method is also referred to as which one of the following?
(a) Minimum strain energy method
(b) Maxwell-Mohr method
(c) Consistent deformation method
(d) Slope-deflection method
Ans. (d)
20. A beam .carries a uniformly distributed load throughout its length. In which of the following configurations will the strain energy be maximum?
(a) Cantilever
(b) Simply supported beam
(c) Propped cantilever
(d) Fixed beam
Ans. (a)
21. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) In slope-deflection method, the forces are taken as unknowns
(b) In slope-deflection method, the joint rotations are taken as unknowns
(c) Slope-deflection method is not applicable for beams and frames having-settlement at supports
(d) Slope-deflection method is also known as force method
Ans. (b)
22. When the effect of wind or earthquake load is considered in the design of rivets and bolts for steel structures, by what percentage the permissible stresses may be exceeded?
(a) 15%
(b) 25%
(c) 33.33%
(d) 50%
Ans. (c)
23. The working range of a crane is limited horizontally for maximum lift only by
(a) Boom length
(b) Length of hoist cable
(c) Length of jib
(d) Counter weight
Ans. (c)
24. What is a tendon profile, in which the eccentricity is proportional to the bending moment caused by any loading on a rigidly supported indeterminate structure, at all cross-sections?
(a) Cable profile
(b) Resultant profile
(c) Concordant profile
(d) Reduced profile
Ans. (c)
25. When power shovels are operated under different site conditions (in terms of material handled), what is the correct sequence in the increasing order of the output for the following materials?
1. Well-blasted rock
2. Hard and tough clay
3. Poorly blasted rock
4. Moist loam or sane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Code:
(a) 1-2-3-4
(b) 1-4-3-2
(c) 4-2-3-1
(d) 4-3-1-2
Ans. (c)
26. For three-dimensional movement of a weight, which one of the following is most suitable?
(a) Chain hoist
(b) Winch
(c) Crane
(d) Jack
Ans. (c)
27. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
List-I (Crane) List-II (Suitable for)
A. Tower crane 1. Hydraulic structures
B. Floating crane 2. High industrial plant
C. Mobile crane 3. Longitudinal and lateral movements of load
D. Gantry crane 4. Railway electrification
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 2 4 1 3
(d) 3 1 4 2
Ans. (a)
28. How are concrete mixers specified?
(a) By the number of cement bags used in a batch
(b) By the nominal volume of concrete that can be mixed in a batch
(c) By the volume of water used
(d) By the volume of aggregate used
Ans. (b)
29. What is the minimum width of roadway for a six-lane high-level bridge constructed for the use of road traffic only?
(a) 21.5 m
(b) 22.5 m
(c) 24.0 m
(d) 25.5 m
Ans. (a)
30. Consider the following statements related to interchanges:
1. In diamond interchange there is the possibility of illegal wrong-way turns.
2. Diamond interchange is far superior to cloverleaf design.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither I nor 2
Ans. (a)
31. If a road surface is adequately supperelevated on horizontal curve, which one of the following is the proper distribution of pressure on the vehicle wheels?
(a) Pressure on both outer and inner wheels is equal
(b) Pressure on inner wheels is more than the outer wheels
(c) Pressure on inner wheels is less than the outer wheels
(d) Pressure on front wheels is thrice the pressure on rear wheels
Ans. (a)
32. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
(Type of Construction) (Binder Content Generally Specified)
A: Bituminous macadam 1. 8—15%
B. Dense bituminous macadam 2. 3—15%
C. Bituminous concrete 3. 4—4.5%
D. Bitumen mastic 4. 4.5—6.0%
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 4 3 2 1
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 4 1 2 3
Ans. (c)
33. If the mean temperature of Sun’s surface is 6000 K and λm of its radiation is 0.5 μm, what is the mean temperature of Earth’s surface for which λm is 10.0 μm, according to Wien’s Displacement Law in Remote Sensing Concept?
(a) 25°C
(b) 28°C
(c) 27°C
(d) 30°C
Ans. (c)
34. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I (Term) List-II (Definition)
A. Apparent solar day 1. The time interval between two successive upper transits of the first point of Aries over the same meridian
B. Sidereal day 2. Time interval between two successive lower transits of the centre of the Sun across the same meridian
C. Tropical year 3. Time interval between two successive passages of the Sun over the meridian of any one of the fixed stars
D. Sidereal year 4. Time interval between two successive vernal equinoxes
Code:
A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 2 1 3 4
(d) 1 2 4 3
Ans. (b)
25. Which one of the following is the correct statement?
A streamlined body is one for which the
(a) Skin friction is zero.
(b) Thickness of the body is less than 1/100 of its length.
(c) Corners are rounded off.
(d) Separation occurs, if at all, at the farthest downstream part of the body
Ans. (d)
36. A flat plate with a sharp leading edge is placed along a free stream of fluid flow. Local Reynolds number at 3 cm from the leading edge is 105. What is the thickness of the boundary layer?
(a) 0.47mm
(b) 0.35 mm
(c) 0.23mm
(d) 0.12mm
Ans. (a)
37. During a flood in a stream of width 200 m (taken as rectangular section), the gauge reading was found to rise by 18 cm per hour. What would be the difference in discharges at two sections, each 250 m on either side of the gauge station?
(a) 10 m3/s less at downstream section
(b) 7.5 m3/s less at downstream section
(c) 5 m3/s less at downstream section
(d) 5 m3/s more at downstream section
Ans. (c)
38. If the stream function PHI = 3x3 — y3, what is the magnitude of velocity at point (2, 2)?
(a) 9
(b) 13
(c) 15
(d) 17
Ans. (d)
39. The weight of aggregate having specific gravity 2.65, completely filled into a cylinder of volume 0.003 m3 is 5.2 kg. What is the value of the angularity index of aggregate (approximately) as given by Murdock?
(a) 1
(b) 0.34
(c) 0.15
(d) 0.05
Ans. (b)
40. Which one of the following criteria is used for obtaining the value of modulus of subgrade reaction from plate bearing test data?
(a) Slope of pressure settlement graph
(b) Pressure corresponding to the settlement 1.25 mm
(c) Deflection corresponding to a pressure of 1.25 kg/ cm2
(d) Pressure corresponding to the settlement of 1.50 mm
Ans. (b)
CIVIL ENGINEERING MCQs
1. What is the area of influence line diagram for the reaction at the hinged end of a uniform propped cantilever beam of span L?
(a) L/8
(b) L/2
(c) L/4
(d) 3L/8
Ans. (c)
2. For a welded plate girder with vertical stiffeners, what is the maximum depth of web provisionable in design when the thickness
of the web plate is 5 mm?
(a) 425 mm
(b) 1000 mm
(c) 1250 mm
(d) 2000 mm
Ans. (b)
3. An ISMB 300 beam has modulus of section of 600 × 103 mm. Plates of 200 mm × 10 mm are added by welding them one on each
flange to have total depth of section 320 mm. What is the section modulus of the plated section?
(a) 462 × 103 mm
(b) 550 × 103 mm3
(c) 710 × 103 mm3
(d) 1220 × 103 mm3
Ans. (d)
4. A column bearing truss in an open industrial shed is 6 m height between its own base and the bottom of the truss. What is the
effective height of the column taken for calculation compressive strength?
(a) 4.8 m
(b) 6.0 m
(c) 7.2 m
(d) 9.0 m
Ans. (a)
5. Which one of the following values represents the maximum slenderness ratio of any connection member which normally acts as a
tie in a roof truss but can be subjected possible reversal of stresses from the action of wind or seismic force?
(a) 150
(b) 200
(c) 250
(d) 350
Ans. (d)
6. A steel plate is 300 mm wide and 10 mm thick. A rivet of nominal diameter of 16 mm is driven into it. What is the net sectional
area of the plate?
(a) 2600 mm2
(b) 2760 mm2
(c) 2830 mm2
(d) 2840 mm2
Ans. (c)
7. A cantilever steel beam of 3 m span carries a uniformly distributed load of 20 kN/m inclusive of self-weight. The beam comprises
of ISLB200 @ 198 N/rn, flange- 100 mm × 7.3 mm; web thickness - 5.4 mm; Ixx = 1696.6 cm4; Iyy = 115.4 cm4. What is the
maximum bending stress in the beam?
(a) 132.62 N/mm2
(b) 530.47 N/mm2
(c) 149.74 N/mm2
(d) 3899.48 N/mm2
Ans. (b)
8. A tension member consists of two angles placed back to back For which one of the following configurations, will the load
carrying capacity of the tension member be maximum?
(a) Gusset palte is in between the two angles and tacking rivets are provided
(b) Gusset plate is in between the two angles and no tacking rivets are provided
(c) Gusset plate is on one side of the two angles and tacking rivets are provided
(d) Gusset plate is on one side of the two angles and no tacking rivets are provided
Ans. (a)
9. In limit state design method, the moment of resistance for a balanced section using M20 grade concrete and HYSD steel of grade
Fe4 15 is given by Mu, tim = Kbd2, what is the value of ‘K’?
(a) 2.98
(b) 2.76
(c) 1.19
(d) 0.89
Ans. (b)
10. How is the deflection in RC beams controlled as per 1S456?
(a) By using large aspect ratio
(b) By using small modular ratio
(c) By controlling span/depth ratio
(d) By moderating water-cement ratio
Ans. (c)
11. At what stress does the first flexural crack appear in RCC beams made of M25’ grade concrete?
(a) 3.0 MPa
(b) 3.5 MPa
(c) 4.0 MPa
(d) 4.5 MPa
Ans. (b)
12. Consider the following statements:
1. When wind load is the primary’ load, no increase in the allowable stresses is provided for in members or fasteners.
2. Due to wind load acting along with dead and live loads, increase in allowable stress upto 33.33% can be provided for.
3. Due to wind load acting along with dead load, increase in allowable stress of 25% in foundation bolts can be provided for.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 only 3
(b) I only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans. (c)
13. A simply supported beam of uniform cross section has span ‘L’ and is loaded by a point load ‘P’ at its mid-span. What is the
length of the elastoplastic zone of the plastic hinge?
(a) L/3
(b) 2L/3
(c) L/2
(d) 3L/3
Ans. (a)
14. Consider the following statements
Torsional restraint in a beam can be achieved by providing.
1. Web or flange cleats at the end connections.
2. External support to the end of the compression flange
3. Bearing stiffness acting in conjunction with the bearing of the beam
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1., 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
15. Considering modular ratio as 13, grade of concrete as M20 and grade of steel as 415, what is the ratio of balanced depth of
neutral axis as per working stress method to the balanced depth of neutral axis as per limit state method?
(a) 12/7
(b) 11/3
(c) 7/12
(d) 3/11
Ans. (c)
16. What is the anchorage value pf a standard hook of a reinforcement bar or diameter D?
(a) 4D
(b) 8D
(c) 12D
(d) 16D
Ans. (d)
17. How is the base-level bending moment of cantilever retaining wall expressed as function of its height H?
(a) H1
(b) H2
(c) H3
(d) H4
Ans. (c)
18. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists
List-I List-II
A. At end support for imposed load 1. 0.5
(not fixed)
B. At inside support, next inner to end 2. 0.55
support, for imposed load (fixed)
C. At end support, for dead load 3. 0.60
and (fixed) imposed load
D. At all other interior supports 4.0.45
(other than at ‘B’) for imposed load (fixed)
5.0.4
Code:
A B C D
(a) 5 3 2 4
(b) 4 2 5 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 5 3 2 1
Ans. (b)
19. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
A. Moment and shear 1. Durability
coefficients
B. Fire resistance 2. Stability
C. Sliding 3. Analysis of structure
D. Span to depth ratio of beam 4. Deflection limits
A B C D
(a) 4 2 1 3
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 3 1 2 4
Ans. (d)
20. What is the adopted maximum spacing between vertical stirrups in an RCC beam rectangular corss-section having an effective depth of 300 mm?
(a) 300 mm
(b) 275 mm
(c) 250 mm
(d) 225mm,
Ans. (d)
(a) L/8
(b) L/2
(c) L/4
(d) 3L/8
Ans. (c)
2. For a welded plate girder with vertical stiffeners, what is the maximum depth of web provisionable in design when the thickness
of the web plate is 5 mm?
(a) 425 mm
(b) 1000 mm
(c) 1250 mm
(d) 2000 mm
Ans. (b)
3. An ISMB 300 beam has modulus of section of 600 × 103 mm. Plates of 200 mm × 10 mm are added by welding them one on each
flange to have total depth of section 320 mm. What is the section modulus of the plated section?
(a) 462 × 103 mm
(b) 550 × 103 mm3
(c) 710 × 103 mm3
(d) 1220 × 103 mm3
Ans. (d)
4. A column bearing truss in an open industrial shed is 6 m height between its own base and the bottom of the truss. What is the
effective height of the column taken for calculation compressive strength?
(a) 4.8 m
(b) 6.0 m
(c) 7.2 m
(d) 9.0 m
Ans. (a)
5. Which one of the following values represents the maximum slenderness ratio of any connection member which normally acts as a
tie in a roof truss but can be subjected possible reversal of stresses from the action of wind or seismic force?
(a) 150
(b) 200
(c) 250
(d) 350
Ans. (d)
6. A steel plate is 300 mm wide and 10 mm thick. A rivet of nominal diameter of 16 mm is driven into it. What is the net sectional
area of the plate?
(a) 2600 mm2
(b) 2760 mm2
(c) 2830 mm2
(d) 2840 mm2
Ans. (c)
7. A cantilever steel beam of 3 m span carries a uniformly distributed load of 20 kN/m inclusive of self-weight. The beam comprises
of ISLB200 @ 198 N/rn, flange- 100 mm × 7.3 mm; web thickness - 5.4 mm; Ixx = 1696.6 cm4; Iyy = 115.4 cm4. What is the
maximum bending stress in the beam?
(a) 132.62 N/mm2
(b) 530.47 N/mm2
(c) 149.74 N/mm2
(d) 3899.48 N/mm2
Ans. (b)
8. A tension member consists of two angles placed back to back For which one of the following configurations, will the load
carrying capacity of the tension member be maximum?
(a) Gusset palte is in between the two angles and tacking rivets are provided
(b) Gusset plate is in between the two angles and no tacking rivets are provided
(c) Gusset plate is on one side of the two angles and tacking rivets are provided
(d) Gusset plate is on one side of the two angles and no tacking rivets are provided
Ans. (a)
9. In limit state design method, the moment of resistance for a balanced section using M20 grade concrete and HYSD steel of grade
Fe4 15 is given by Mu, tim = Kbd2, what is the value of ‘K’?
(a) 2.98
(b) 2.76
(c) 1.19
(d) 0.89
Ans. (b)
10. How is the deflection in RC beams controlled as per 1S456?
(a) By using large aspect ratio
(b) By using small modular ratio
(c) By controlling span/depth ratio
(d) By moderating water-cement ratio
Ans. (c)
11. At what stress does the first flexural crack appear in RCC beams made of M25’ grade concrete?
(a) 3.0 MPa
(b) 3.5 MPa
(c) 4.0 MPa
(d) 4.5 MPa
Ans. (b)
12. Consider the following statements:
1. When wind load is the primary’ load, no increase in the allowable stresses is provided for in members or fasteners.
2. Due to wind load acting along with dead and live loads, increase in allowable stress upto 33.33% can be provided for.
3. Due to wind load acting along with dead load, increase in allowable stress of 25% in foundation bolts can be provided for.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 only 3
(b) I only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans. (c)
13. A simply supported beam of uniform cross section has span ‘L’ and is loaded by a point load ‘P’ at its mid-span. What is the
length of the elastoplastic zone of the plastic hinge?
(a) L/3
(b) 2L/3
(c) L/2
(d) 3L/3
Ans. (a)
14. Consider the following statements
Torsional restraint in a beam can be achieved by providing.
1. Web or flange cleats at the end connections.
2. External support to the end of the compression flange
3. Bearing stiffness acting in conjunction with the bearing of the beam
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1., 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
15. Considering modular ratio as 13, grade of concrete as M20 and grade of steel as 415, what is the ratio of balanced depth of
neutral axis as per working stress method to the balanced depth of neutral axis as per limit state method?
(a) 12/7
(b) 11/3
(c) 7/12
(d) 3/11
Ans. (c)
16. What is the anchorage value pf a standard hook of a reinforcement bar or diameter D?
(a) 4D
(b) 8D
(c) 12D
(d) 16D
Ans. (d)
17. How is the base-level bending moment of cantilever retaining wall expressed as function of its height H?
(a) H1
(b) H2
(c) H3
(d) H4
Ans. (c)
18. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists
List-I List-II
A. At end support for imposed load 1. 0.5
(not fixed)
B. At inside support, next inner to end 2. 0.55
support, for imposed load (fixed)
C. At end support, for dead load 3. 0.60
and (fixed) imposed load
D. At all other interior supports 4.0.45
(other than at ‘B’) for imposed load (fixed)
5.0.4
Code:
A B C D
(a) 5 3 2 4
(b) 4 2 5 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 5 3 2 1
Ans. (b)
19. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II
A. Moment and shear 1. Durability
coefficients
B. Fire resistance 2. Stability
C. Sliding 3. Analysis of structure
D. Span to depth ratio of beam 4. Deflection limits
A B C D
(a) 4 2 1 3
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 3 1 2 4
Ans. (d)
20. What is the adopted maximum spacing between vertical stirrups in an RCC beam rectangular corss-section having an effective depth of 300 mm?
(a) 300 mm
(b) 275 mm
(c) 250 mm
(d) 225mm,
Ans. (d)
APPSC Assistant Architectural Draughtsman & Surveyors Written Test Patten & Syllabus
APPSC Asst. Architectural Draughtsman and Surveyors in A.P. Town Planning Sub-service (Notification No. 48/ 2008) Written Exam will be held on 24/07/2011 FN & AN. Assistant Architectural Draughtsman & Surveyors Selection Procedure, Written Exam Paper Patten & Syllabus is given below.
Selection Process: Written Test & Interview
APPSC Asst. Architectural Draughtsman & Surveyors Written Test Patten
| Paper | Subject | Questions | Marks | Duration |
| PART-A (WRITTEN EXAMINATION – Objective type) | ||||
| Paper-1 | GENERAL STUDIES (SSC standard) | 150 | 150 | 150 Minutes |
| Paper-2 | SUBJECT:(Intermediate vocational standard) | 150 | 150 | 150 Minutes |
| PART-B INTERVIEW - 30 Marks | ||||
APPSC Assistant Architectural Draughtsman & Surveyors Syllabus
PAPER-1: General Studies Syllabus
Syllabus formulated by the Board of Secondary School Certificate, A.P., as prescribed for 10th Class in History, Geography, Civics, Economics, Physics, Chemistry, Botany, Zoology and Current Affairs.
PAPER-2: -Subject Syllabus
Importance of Lettering and Numbering – Figure Sizes and Proportions IS Standard Practice.
Construction of Plain Geometric Figures (Lines Angles, Triangle, Rhombus, Quadrilaterals, Polygon etc) Orthographic Projection- Recommended methods of Projections as per IS code.
Construction of Ordinary Scale – Plain, & Comparative Diagonal, Vernier, & Scale of Chords.
Drawing Plan and Elevation of Points, Lines, Surfaces & Solids.
Conventional Signs and Symbols as per IS Code for Engineering Drawings and Buildings Drawings.
Drawing and detailing of (a) Brick arrangements – Various types of Bonds, (b) Stone Masonry & Stone Joints ((c) Foundations – Various types (d) Damp Proof Course & Plinth Protection (e) Roof types – Reinforced Concrete, Madras Terrace & Jack Arch, (f) Flooring types – Timber Flooring, Steel Flooring, Tile Flooring, (g) Arches & Lintels Carpentry Joints, Framing, Paneling and Moulding (h) Doors types – Paneled, Glazed, and Flush Door, (i) Windows & Ventilators (j) Pitched Roof – Various types – King post, & Queen post, (k) Steel Roof Trusses (l) Stairs – Various types – Wooden, Steel and Reinforced Concrete – Spiral, Doglegged & Open Well (m) Single Storied Residential House – Plan, Elevation and Section (n) Cross section showing different types of Roads, Railway Track, Embankment and layout of Platforms (o) Different types of Irrigation Structures (p) Pipelines Joints Drainage Works, Manholes, Sanitary fittings, (q) Forms of Rivet Heads, Types of Riveted Joints, Standard Steel Section, Standard Connections.
Surveying of Buildings Sites with Chain, Field Book Entries – Plotting – Calculation of Areas.
Use of Prismatic Compass, Handling of Leveling Instrument – Differential Leveling, Surveying of Building Sites with Chain and Level for Calculation of Earth Work. Plotting of Longitudinal/ Cross section, Drawing of Contours.
Thursday, July 14, 2011
APPSC ASSISTANT ARCHITECTURAL DRAUGHTSMAN & SURVEYOR EXAM STUDY MATERIAL
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
1 The selection of the front view in executing a multiview drawing of an object is dependent upon the following factors:
A) size and shape of the object and their relationship to all views.
B) the number of principal views required and the related auxiliary views needed to describe the object.
C) the greatest contour shape, the related dashed lines, and the position of use.
D) the size of the object, size of the paper, position of use, and least number of hidden lines.
Ans: (d)
2 All of the following statements about multiview drawings are true, except:
A) each view is a 3-D pictorial image
B) based on orthographic projection
C) at least two views of the object
D) views are defined by planes of projection
Ans: (a)
3 Which type of projection does not have the projection rays parallel to each other?
A) axonometric projection
B) oblique projection
C) orthographic projection
D) perspective projection
Ans: (d)
4 Which is not a principal view?
A) bottom
B) left side
C) auxiliary
D) front
Ans: (c)
5 Principle planes will appear as:
A) normal planes or edges
B) oblique planes or edges
C) normal planes or oblique planes
D) skewed planes or edges
Ans: (a)
6 In orthographic projection, visual rays or lines of sight for a given view are _____________ to each other.
A) perpendicular B) oblique
C) normal D) parallel
Ans: (d)
7 What two types of projections give a pictorial view of the object without convergence?
A) orthographic and perspective
B) oblique and axonometric
C) perspective and oblique
D) isometric and orthographic
Ans: (b)
8 Inclined planes in a three-view drawing will appear as:
A) two surfaces and one edge
B) two edges and one surface
C) three edges
D) foreshortened in each view
Ans: (a)
9 Oblique planes in a three-view drawing will appear as:
A) two surfaces and one edge
B) two edges and one surface
C) three edges
D) three surfaces
Ans: (d)
10 Normal planes in a three-view drawing will appear as:
A) one surface and two edges
B) three surfaces
C) one edge and two surfaces
D) three edges
Ans: (a)
11 A viewing direction which is perpendicular to the surface in question gives a(n) ____________ view.
A) inclined
B) normal
C) oblique
D) perspective
Ans: (b)
12 A viewing direction which is parallel to the surface in question gives a(n) ____________ view.
A) inclined
B) normal
C) edge
D) perspective
Ans: (c)
13 When a surface of an object is inclined to a plane of projection, it will appear _________________ in the view.
A) foreshortened
B) in true size and shape
C) as a line
D) as a point
Ans: (a)
14 What are the three principle planes in orthographic projection?
A) front, top, profile
B) back, top, profile
C) top, front, right side
D) frontal, horizontal, profile
Ans: (d)
15 The top view of an object should typically be drawn:
A) to the right of the front view.
B) anywhere on the same page.
C) directly above the front view.
D) on a separate piece of paper.
Ans: (c)
16 A horizontal surface of a multiview drawing will appear as a(n) ___________ in the front view.
A) edge
B) normal surface
C) point
D) foreshortened surface
Ans: (a)
17 Which view is usually developed first, contains the least amount of hidden lines, and shows the most contours in multiview drawings?
A) right side B) top
C) back D) front
Ans: (d)
18 A sphere can be described in how many views?
A) 4 B) 3
C) 2 D) 1
Ans: (d)
19 An asymmetric object is usually described by how many views?
A) 6 B) 3
C) 4 D) 2
Ans: (b)
20 An axially symmetric object, such as one turned on a lathe, normally can be shown in _________ view(s).
A) one B) two
C) three D) four
Ans: (b)
21 In orthographic projection, visual rays are __________ to the projection plane.
A) parallel B) adjacent
C) perpendicular D) tangent
Ans: (c)
22 The top and right side views have what common dimension(s)?
A) height and width
B) width and depth
C) height
D) depth
Ans: (d)
23 For orthographic projection, the engineering custom in the United States dictates the use of:
A) first-angle projection
B) second-angle projection
C) third-angle projection
D) fourth-angle projection
Ans: (c)
24 For orthographic projection, the engineering custom in Europe dictates the use of:
A) first-angle projection
B) second-angle projection
C) third-angle projection
D) fourth-angle projection
Ans: (a)
25 The sequence for the direction of view (or line of sight) for any orthographic projection as utilized in the United States is:
A) eye of observer>projection plane>object
B) eye of observer>object>projection plane
C) projection plane>object>eye of observer
D) projection plane>eye of observer>object
Ans: (a)
26 Depending on its relationship to the projection plane on which the view is projected, a line may project:
A) true length
B) foreshortened
C) as a point
D) all of the above
Ans: (d)
27 If a surface on an object is parallel to one of the principal planes of projection, then the angular relationship of that surface to at least two other principal projection planes is:
A) parallel
B) perpendicular
C) inclined
D) unknown
Ans: (b)
28 Good practice dictates that the characteristic contour shape of the object be shown in what view?
A) top
B) front
C) right side
D) any side
Ans: (b)
29 The height, width, and depth of an object can be shown with a minimum of how many orthographic projection views?
A) six
B) three
C) two
D) four
Ans: (c)
30 Which of the following pairs of orthographic views both show the height dimension?
A) left side and front
B) top and front
C) top and rear
D) bottom and right side
Ans: (a)
31. Hidden lines are drawn as
(a) dashed narrow lines
(b) dashed wide lines
(c) long-dashed dotted wide line
(d) long-dashed double dotted wide line
Ans: (a)
32. Line composed of closely and evenly spaced short dashes in a drawing represents
(a) visible edges
(b) hidden edges
(c) hatching
(d) pitch circle of gears
Ans: (b)
33. Lettering on a drawing sheet should have
(a) all alphabets in capital letters
(b) all alphabets in small letters
(c) In a sentance only first alphabet in capital letter
(d) In a sentance only abbreviations are capital letter
Ans: (a)
34. The line connecting a view to note is called
(a) dimension line
(b) projection line
(c) leader
(d) arrowheads
Ans: (c)
35. The dimension figure for radius of a circle should be preceded by
(a) R
(b) CR
(c) SR
(d) RAD
Ans: (b)
36. The recommended method of dimensioning a sphere with diameter 80 mm is
(a) 80fS
(b)f80S
(c) S80f
(d) Sf80
Ans: (d)
37. Methods of arrangement of dimensions includes
(a) Parallel, continuous and combined
(b) Perpendicular, parallel and combined
(c) Perpendicular, continuous and combined
(d) Perpendicular, parallel and continuous
Ans: (a)
38. Superimposed dimensioning is a simplified method of
(a) chain dimensioning
(b) parallel dimensioning
(c) combined dimensioning
(d) tabular dimensioning
Ans: (b)
39. A curve drawn for Boyle’s law (PV = constant) on a P-V chart has a characteristic shape of
(a) ellipse
(b) parabloa
(c) oblique hyperbola
(d) rectangular hyperbola
Ans: (d)
40. The profile of a gear teeth is in the form of
(a) parabola
(b) involute
(c) spiral
(d) helix
Ans: (b)
41. When two angles together make 90º, they are called
(a) obtuse angle
(b) reflex angle
(c) complementary angles
(d) supplementary angles
Ans: (c)
42. The included angle of a hexagon is
(a) 300
(b) 600
(c) 1200
(d) 1500
Ans: (c)
43. The curve generated by a point on the circumference of a circle, which rolls without slipping along outside of another circle is known as
(a) Hypocycloid
(b) Epicycloid
(c) Cycloid
(d) Trochoid
Ans: (b)
44. In orthographic projections, the rays are assumed to
(a) diverge from station point
(b) converge from station point
(c) be parallel
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
45. If an object lies in third quadrant, its position with respect to reference planes will be
(a) infront of V.P, above H.P
(b) behind V.P., above H.P.
(c) behind V.P., below H.P.
(d) infront of V.P., below H.P.
Ans: (c)
46. If the Vertical Trace (V.T.) of a line lies 30 mm above reference line (XY), then its position will be
(a) 30 mm infront of V.P.
(b) 30 mm behind V.P.
(c) 30 mm above H.P.
(d) 30 mm below H.P.
Ans: (c)
47. When an object is cut by a section plane parallel to H.P and perpendicular to V.P, then the sectional view of the object is obtained in
(a) top view
(b) front view
(c) left side view
(d) right side view
Ans: (a)
48. Which of the following object gives a circular section, when it is cut completely by a section plane (irrespective of the angle of the section plane)
(a) Cylinder
(b) Sphere
(c) Cone
(d) Circular lamina
Ans: (b)
49. Comparative scale is a pair of scale having a common
(a) units
(b) representative fraction
(c) length of scale
(d) least count
Ans: (b)
50. An angle can be set off and measured with the help of
(a) plane scale
(b) diagonal scale
(c) comparative scale
(d) Scale of chords
Ans: (d)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)